
Executive Summary:
Saudi Arabia’s Vision
2030 seeks to achieve the sixth Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 6): ensuring
availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. This
is pursued through integrated policies and strategies that address the challenges
of water scarcity and rising demand, recognizing water as one of the most vital
natural resources for economic and social development.
The Vision emphasizes
improving water-use efficiency, expanding desalination projects, and advancing
recycling and treatment technologies to ensure the sustainability of water
resources and meet the needs of current and future generations. Key priorities
include investing in clean energy-based desalination technologies, developing
nationwide water and sanitation networks, and promoting community awareness
programs to foster a culture of conservation.
Vision 2030 also aims
to achieve balanced development across the Kingdom by enhancing water and
sanitation infrastructure, ensuring equitable distribution of water resources,
and reducing disparities between urban and rural areas. Moreover, Saudi Arabia highlights
the importance of partnerships with the private and non-profit sectors in water
management and the implementation of innovative projects that improve
efficiency and reduce waste.
Through these
efforts, the Kingdom reaffirms its commitment to sustainable development by
enhancing water and sanitation security, in alignment with Vision 2030 and the
United Nations Sustainable Development Agenda.
Within this
framework, Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University plays a significant role
in supporting SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) by implementing advanced water
management systems on campus, such as greywater reuse networks, efficient
irrigation systems, and wastewater treatment facilities. The university also
organizes awareness programs and specialized workshops on water conservation
and sustainability, while supporting scientific research in the fields of water
security and sustainable technologies.
In doing so, the
university continues to uphold its environmental and social responsibility by
promoting a culture of sustainable water use and contributing practical
solutions to water challenges, reflecting its leadership in achieving the
ambitions of Vision 2030.
Water Tower to Supply the University with Free Drinking Water:
 The water tower comprises a free drinking water reservoir that
supplies the entire university city with between 8,000 and 10,000 cubic meters
of drinking water daily, in addition to a reservoir designated for irrigation
purposes, a drinking water treatment plant, and a fire-fighting network serving
the educational area, faculty housing, and King Abdullah City for Female
Students. Furthermore, there is a greywater network responsible for converting
water from sinks and washbasins into treated water suitable for reuse, thereby
contributing to environmental sustainability.
The water tower comprises a free drinking water reservoir that
supplies the entire university city with between 8,000 and 10,000 cubic meters
of drinking water daily, in addition to a reservoir designated for irrigation
purposes, a drinking water treatment plant, and a fire-fighting network serving
the educational area, faculty housing, and King Abdullah City for Female
Students. Furthermore, there is a greywater network responsible for converting
water from sinks and washbasins into treated water suitable for reuse, thereby
contributing to environmental sustainability.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r4vyl6FZ4ug
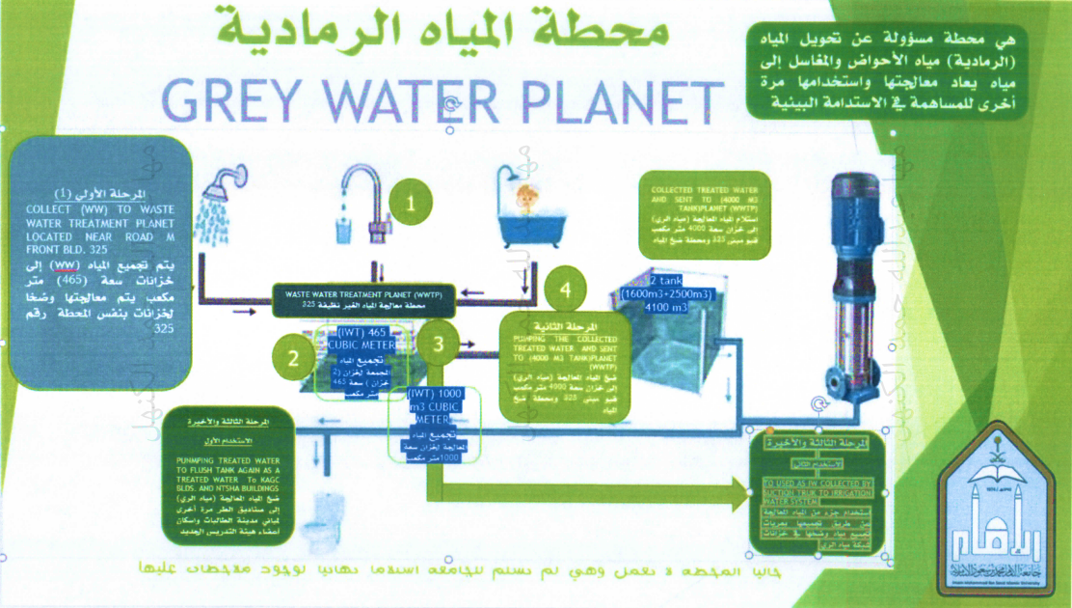
Wastewater Treatment Processes:
Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University
has an established and advanced wastewater treatment system that forms an
integral part of the environmental infrastructure within the university city.
This initiative is part of the university’s ongoing efforts to conserve water
and ensure its sustainability, in alignment with global standards for water
management, with the aim of protecting the environment and enhancing public
health.
The system includes the following components:
- Greywater Network that
collects water from sinks and washbasins, in addition to a sewage collection
network that transports wastewater to the treatment plant.
- Water Treatment Plant
that converts greywater and sewage into treated water suitable for reuse.
- Mechanical Treatment
through coarse and fine filtration systems to remove large and small particles
from the water.
- Biological Treatment
using advanced aeration and sedimentation processes to break down organic
matter and make the water safe for reuse.
- Final Filtration and Disinfection
by passing the water through sand filters followed by chlorination to ensure
its safety.
- Sustainable Use of Treated Water
for purposes such as irrigation and cooling systems, thereby contributing to
the preservation of water resources and supporting environmental
sustainability.
As a public university, Imam Mohammad
Ibn Saud Islamic University adheres to the mechanism approved by the National
Center for Water Efficiency and Conservation, ensuring compliance with national
best practices in water resource management and consumption efficiency.
https://maee.gov.sa/sites/AR/EvidenceAndRegulations/Lists/EvidenceAndProcedures/Attachments/14/Grey%20Water%20Re-Use%20Final_Arabic%20V8.1_28_08_2023.pdf
University Procedures to Prevent Contaminated Water from
Entering the Water System:
Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud
Islamic University implements
comprehensive technical procedures and systems designed to prevent the entry of
contaminated water into the university’s water network, including contamination
resulting from accidents or accidental leaks. These measures ensure the safety
of water supplies and the continuity of distribution in accordance with the
highest quality standards.
The procedures include:
- Drinking Water Treatment and Purification
Plant that monitors water quality and removes any
contaminants before distribution into the network.
- Integrated Mechanical and Biological
Filtration Systems at the treatment plant to ensure
compliance with safety standards.
- Chlorination as a final
stage before distribution to ensure water is free from bacteria and viruses.
- Separation of Greywater Networks from Drinking Water Networks to prevent any cross-contamination.
- Fire-Fighting Network and Emergency
Response System to maintain the supply of clean water during
incidents.
- Rapid Response Protocols
that include stopping the pumping of water from any source suspected of
contamination and conducting immediate quality tests.
- Routine Maintenance of Pumps
in the wastewater treatment system, considered essential to ensure operational
continuity and maintain the system’s effectiveness and efficiency. This
maintenance is carried out regularly according to a defined schedule—weekly,
monthly, or annually—depending on the type of pumps, their usage, and the load
they handle.



As part of its commitment to applying the highest standards of
quality and sustainability in facilities management, Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud
Islamic University collaborates with Arabian Maintenance
Operations Services (AMOS), a leading national company in the
field of operations, maintenance, and facilities management. The company has
executed several strategic projects within the university campus, including operation, maintenance, and cleaning of the University City and
King Abdullah City for Female Students, as well as the
development of specialized systems and the rehabilitation of student housing
facilities.
The scope of AMOS’s work includes providing advanced services in water resource management, where the
university benefits from the company’s expertise in measuring
the quantities of reused water across all its facilities.
This is part of the university’s efforts to optimize water usage and minimize
waste, through accurate tracking of treated water volumes used for irrigation
and cooling purposes, ensuring improved resource efficiency and promoting
sustainable practices.
This collaboration reflects the university’s approach to
integrating advanced technological solutions in infrastructure management, in
alignment with Saudi Vision 2030 and
the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG
6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG
12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
University Policy and Practices to Increase Water Reuse:

As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability and
efficient water resource management, Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud
Islamic University implements advanced practices aimed at
increasing water reuse across its facilities. These efforts include operating
the Water Tower, which contains
a greywater network that treats water from sinks and washbasins for reuse in
irrigation, as well as a comprehensive
wastewater treatment system that utilizes treated water for
irrigation and cooling purposes. The university also collaborates with Arabian Maintenance Operations Services (AMOS) to
accurately measure the quantities of reused water, ensuring improved efficiency
and reduced waste.
On the awareness level, the university has adopted an Environmental Awareness Initiative that places
significant focus on water reuse, through
awareness campaigns, workshops, and educational programs targeting students,
staff, and the broader campus community. These activities aim to promote a
culture of water conservation and encourage sustainable practices in daily
life.
These initiatives align with Saudi Vision 2030
and the United Nations Sustainable Development
Goals, particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water and
Sanitation) and SDG 12 (Responsible
Consumption and Production), reinforcing the university’s
position as a leading educational institution in adopting sustainable
solutions.
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1836060542768738596
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1835404561374138531

Sustainable Landscaping, Green Space
Projects, and Planting Drought-Resistant Plants at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud
Islamic University
https://imamu.edu.sa/news/Pages/news-22-9-1442-02.aspx
https://x.com/IMSIU_edu_sa/status/1899074398495129643
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1866542128681177343
https://x.com/IMSIU_edu_sa/status/1898030120423587851/photo/1
As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability and in
alignment with Saudi Vision 2030
targets, Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University, under the patronage of its
President, Prof. Ahmed bin Salem Al-Ameri, launched on Monday, 21 Ramadan 1442
AH, the Faculty and Staff Housing Afforestation
Project in coordination with the Saudi
Green Initiative—announced by His Royal Highness Prince
Mohammed bin Salman, Crown Prince, Deputy Prime Minister, and Minister of
Defense—and in collaboration with the Riyadh Green Project.
The project aims to improve the quality of life within university housing,
increase the percentage of green spaces, and intensify tree planting across
various areas of the university city.
The university also launched, with the participation of the
President, an afforestation initiative for student
housing, involving the planting of 3,000
trees as part of a broader plan to plant 100,000
trees within the university city, supporting the Saudi Green Initiative and enhancing green
infrastructure while reducing water consumption.
The university implements landscaping practices designed to reduce
water consumption, including climate-responsive landscape design and the
selection of low-water-use plants
such as Alphitonia, Jujube, Bougainvillea, and Sedges. These plants contribute
significantly to environmental sustainability by reducing water usage,
conserving energy, and minimizing soil and water pollution. They help alleviate
pressure on the university’s treated water sources, preserve biodiversity,
improve air quality, support local ecosystems, and mitigate the effects of
drought—making them a vital choice for sustainable environmental practices.
According to Prof. Al-Ameri,
these initiatives form the foundation of the university’s larger “Green University” program, which seeks to make the campus
environmentally friendly by increasing green areas, improving energy
efficiency, and providing recreational and walking spaces—supporting the
success of the Saudi
Green Initiative and
the Middle East Green
Initiative. As noted by
Eng. Shafi Al-Qahtani, General Supervisor of Technical Affairs, the university
aims to plant 12,300
trees, of which 2,600 have been planted to date, in collaboration
with the Riyadh Green Project. Through these efforts, the university also seeks
to promote community awareness of afforestation, optimize energy use, and
reduce paper consumption across its facilities.


Teaching the Principles of Good Water Management at
Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University:
Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud
Islamic University is committed to promoting awareness and knowledge of the
principles of good water management within its academic programs and community
initiatives, in alignment with the objectives of Saudi Vision 2030 and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). The university provides learning
opportunities for both the campus and local communities through multiple
academic disciplines, including Architecture, which focuses on integrating water management principles into building
and landscape design, selecting materials and technologies that contribute to
conservation, reuse, rainwater harvesting, and smart irrigation systems.
 Other
relevant disciplines include Environmental
Engineering,
Civil Engineering, and Environmental Science and Natural Resource
Management,
where students are trained in efficient water management methods, protecting
water sources from pollution, and designing treatment and reuse systems.
Through this interdisciplinary approach, the university helps prepare
graduates capable of developing sustainable solutions for water resource
management at both local and global levels.
Other
relevant disciplines include Environmental
Engineering,
Civil Engineering, and Environmental Science and Natural Resource
Management,
where students are trained in efficient water management methods, protecting
water sources from pollution, and designing treatment and reuse systems.
Through this interdisciplinary approach, the university helps prepare
graduates capable of developing sustainable solutions for water resource
management at both local and global levels.
https://units.imamu.edu.sa/colleges/Engineering/AcademicDepts/Pages/architectural_engineering.aspx
The relationship between Architecture
and learning the principles of good water management is particularly strong, as
architects are not limited to designing the physical appearance of buildings
but also plan water use systems
inside and outside the building to achieve efficiency and sustainability. This
relationship can be illustrated in several key areas:
- Designing Water-Efficient Buildings
- Integrating water-saving
technologies into architectural design, such as selecting water-efficient
fixtures and greywater reuse systems.
- Designing roofs and systems
for rainwater harvesting to
be used for irrigation or cleaning.
- Landscape Planning
- Selecting low-water-use
plants in outdoor designs and implementing smart irrigation systems with
moisture sensors.
- Arranging green spaces to
minimize the need for frequent irrigation.
- Water Management in Building Infrastructure
- Incorporating on-site
wastewater treatment systems in large projects.
- Designing water pathways
that minimize loss, preserve water quality, and prevent contamination.
- Meeting Environmental Standards
- Adhering to green building standards
such as LEED or BREEAM,
which include specific requirements for water efficiency and management.
- Contributing to the
achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals,
especially SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation).
- Architectural Education and Water
- Including courses on water
management within architecture programs, enabling students to learn water
management principles as part of sustainable design for buildings and urban
areas.
- Training students through
practical projects that link architectural design with innovative water
management solutions, particularly in arid or drought-prone environments.
The Rural Development course is directly related to learning the
principles of good water management, as rural communities rely heavily on water
resources for agriculture, livestock farming, domestic uses, and handicraft
industries. Through teaching this course, students learn how to manage these
resources efficiently to ensure their sustainability and to support the
economic and social development of rural areas.

https://isd.imamu.edu.sa/soc/d2/SiteAssets/Pages/program/خطة%20برنامج%20الماجستير%20علم%20اجتماع.pdf
The main areas of connection are as follows:
- Water Resource Management in Rural Agriculture
- Applying modern irrigation
methods (such as drip or sprinkler irrigation) to optimize water use.
- Scheduling irrigation
according to crop needs, soil conditions, and climate.
- Protection of Rural Water Sources
- Protecting wells and
springs from contamination.
- Monitoring the quality of
water used for drinking and agriculture.
- Water Reuse
- Utilizing greywater or
treated water for crop irrigation or landscaping.
- Developing rainwater
harvesting and storage projects.
- Planning and Sustainable Development
- Integrating water
management into rural development plans to ensure resource continuity.
- Involving the local
community in setting policies and implementing sustainable water practices.
- Education and Training
- Providing training programs
for farmers and community members on efficient water use.
- Teaching students how to
assess water needs in rural projects and design practical solutions.
The University Actively Promotes
Conscious Water Consumption:
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1804909160133210336
https://units.imamu.edu.sa/vrectorate/TA/announcements/Pages/26-3-2020.aspx
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1810899515190231264
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1810221184341991792
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1808441732477899164
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1807638806591385631
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1805881514430718281
https://x.com/TA_imamu/status/1805118833704779984

Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University actively promotes a
culture of conscious water consumption by adopting a range of initiatives and
practices aimed at improving the efficiency of water use and reducing waste, in
alignment with Saudi Vision 2030 and
the United Nations Sustainable Development
Goals, particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water and
Sanitation).
These efforts include implementing water
reuse projects through greywater networks and a wastewater
treatment plant, utilizing treated water for irrigation and cooling purposes,
thereby reducing reliance on freshwater sources. The university also landscapes
its green areas in ways that minimize water consumption, such as selecting
low-water-use plants—like Alphitonia, Jujube, Bougainvillea, and Sedges—planted
as part of the afforestation project in collaboration with the Saudi
Green Initiative and the Riyadh
Green Project.
On the awareness
front, the university conducts environmental
awareness initiatives that include educational campaigns and
workshops for students and staff, aimed at enhancing understanding of good
water management practices and the importance of conservation, thus
contributing to building a community-wide commitment to water sustainability.
The University’s Participation in
Water Conservation Efforts Beyond Campus:
Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University actively participates in
water conservation and protection efforts beyond its campus, engaging in
national and community initiatives that promote environmental sustainability
and the efficient use of water resources. Among its notable contributions is
the university’s collaboration with the Saudi
Green Initiative and the Riyadh
Green Project, which includes tree planting and the use of
low-water-consumption plants—activities that extend their impact beyond the
campus to improve the local environment and enhance vegetation cover in Riyadh.
https://imamu.edu.sa/news/pages/news-25-04-1443_2.aspx?utm_source=chatgpt.com
The university also takes part in national campaigns such as the “100,000 Trees Initiative”, which aims for
large-scale afforestation, contributing to water conservation by reducing
surface runoff, improving soil quality, and increasing moisture retention
capacity.
https://www.spa.gov.sa/N2278610?utm_source=chatgpt.com
As part of its awareness-raising efforts, the university’s Technical Affairs Department, represented by
its Media and Communication Unit, launched a Water
Consumption Rationalization Campaign in collaboration with
the National Center for Water Efficiency and
Rationalization, aimed at achieving water sustainability and
conserving natural resources. This campaign began on Tuesday, January 4, 2020,
and was delivered through multiple communication channels, including the
department’s official Twitter account, official website, and display screens
inside university facilities.
https://units.imamu.edu.sa/vrectorate/TA/News/Pages/23-1-2022-4.aspx
In addition, the Saudi Water Authority,
represented by its training arm, the Water Academy,
signed a Memorandum of Understanding
with Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University, represented by the College of
Business, to enhance cooperation in scientific research, training, and
capacity-building in the water sector. The agreement includes supporting
academic cooperation projects through the implementation of specialized
training programs, exchanging expertise and knowledge, organizing related
conferences, seminars, and workshops, and developing educational initiatives
that contribute to preparing national talent, meeting labor market needs, and
fostering innovation in water resource management. This partnership embodies
the Authority’s commitment to strengthening collaboration with academic
institutions, leveraging human capital, building capacity, and supporting
sustainability objectives by preparing qualified professionals capable of
addressing sector challenges.
🔗 Details of the
Agreement on the National Center for Water Efficiency and Rationalization
Website

Sustainable Infrastructure at the
University:
The university has
integrated sustainability principles into its infrastructure by establishing
smart irrigation systems and using modern technologies for recycling treated
water. These systems serve as live educational tools for students, allowing
them to witness the practical application of water sustainability in real life,
which enhances their understanding of the importance of these practices.